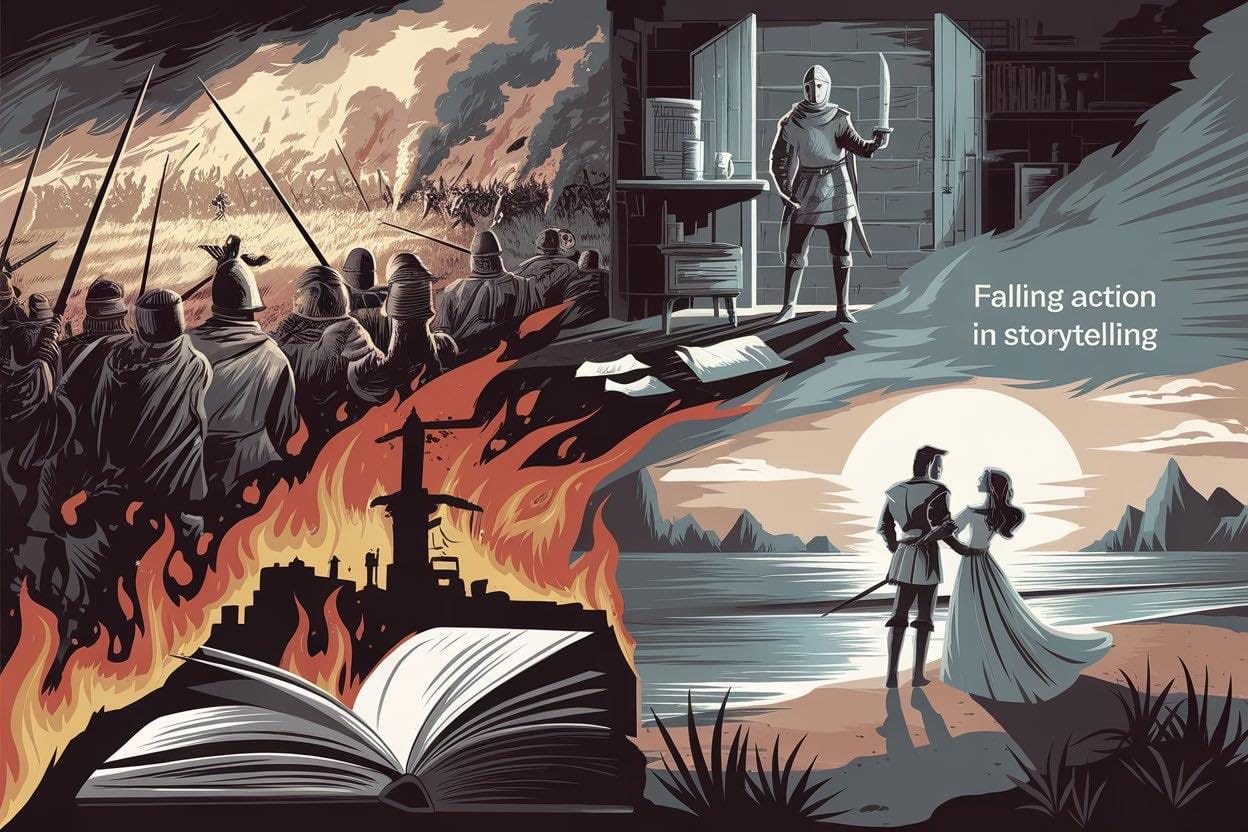
In narrative structure, the falling action represents the necessary consequence of the climax. This essential phase moves the narrative forward by ensuring that the story’s central conflicts achieve their resolution and that its characters confront the results of pivotal events. It follows the climax in structures like Freytag’s Pyramid, where it addresses unanswered elements and subordinate narrative threads. This segment provides the closure that completes the story.
The Structural Role of Falling Action
Falling action binds the climax to the narrative’s conclusion, ensuring a seamless narrative flow. Without this phase, a story risks abrupt transitions that can confuse or disengage the audience. It also helps resolve secondary conflicts or subplots that might otherwise undermine the narrative’s cohesion.
In stories with multiple plotlines, the falling action merges these separate arcs into a single, unified ending. Authors use this phase to balance various narrative elements while constructing a complete whole. Whether the tone is contemplative, triumphant, or solemn, the falling action prepares the audience for the story’s closure.
Role in Plot and Character Development
Falling action is essential for character arcs and plot development. It reveals the outcomes of decisive choices and actions. This revelation shows the full extent of a character’s change. The phase often includes moments for internal examination or the mending of relationships, which add substance to the narrative.
The balance and clarity provided by falling action are integral to narrative pacing. By easing the transition from intense climactic events to resolution, it maintains the story’s progression and prevents sudden shifts that could disorient the audience.
Examples from Classic and Modern Literature
- J. R. R. Tolkien’s The Lord of the Rings (1954): Frodo Baggins’s return to the Shire after the One Ring’s destruction reestablishes a state of order. The period offers the characters and readers a necessary pause to reflect on the saga’s events before the final closure.
- Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird (1960): The events after Tom Robinson’s trial force Scout Finch to confront harsh realities wherein she must process the trial’s outcome and the prejudice within her community. This period is necessary for her moral development and the novel’s examination of society.
- Charles Dickens’s A Christmas Carol (1843): Ebenezer Scrooge exhibits profound behavioral change after being visited by the ghosts. The falling action focuses on his changed behavior, which solidifies the story’s ethical argument and completes his personal journey.
- William Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet (1597): The tragic deaths of Romeo and Juliet compel their feuding families to reconcile. This peace between the Montagues and Capulets presents the dire cost of their conflict. The falling action reinforces the play’s central ideas about love and fate.
- Suzanne Collins’s The Hunger Games (2008): Katniss Everdeen’s return to District 12 follows the ordeal of the Games and initiates an examination of the psychological damage from violence and survival. This falling action explores the broader social systems that enable such events.

Key Roles of Falling Action
In each of these examples, the falling action serves a vital role in the following ways:
- Easing tension: The falling action lowers the narrative and emotional intensity that peaks at the climax.
- Resolving conflicts: Loose ends are tied up and conflicts are addressed, leading to a sense of closure.
- Developing characters: Characters often undergo defining change during the falling action that assimilates their experiences and arrives at new realizations.
- Reinforcing themes: The falling action can emphasize the story’s central themes and provide a final opportunity for the author to deliver their message.
- Providing resolution: The falling action ensures that the ending feels both satisfying and meaningful.
Further Reading
What is Story Structure? 8 Types You Should Know by Grammarly
Falling Action: Definition and Why Falling Action Doesn’t Exist In Most Stories by Joe Bunting, The Write Practice
What is the FALLING ACTION of a story? by Sped Sheets, YouTube
How to write the climax/falling action? on Reddit




